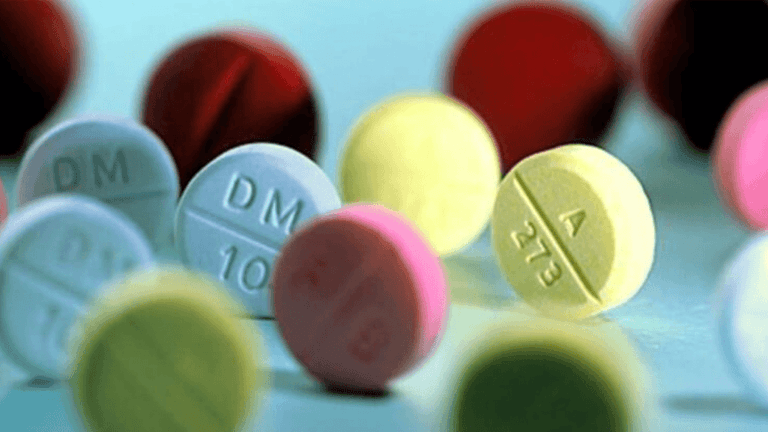
Struggling to get a good night’s sleep can be frustrating and exhausting, leaving you feeling groggy and unproductive the next day. While prescription sleep aids may seem like the only solution, there are various over the counter sleeping pills and natural sleep supplements that can help you achieve better rest without the need for a doctor’s visit.
These OTC sleep remedies, ranging from antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and doxylamine (Unisom) to natural options such as melatonin and valerian root, can be effective for occasional sleepless nights. However, it’s important to note that they are not intended for long-term use and may cause side effects like drowsiness the following day.
When exploring alternative sleep solutions, it’s essential to consider factors such as the active ingredients, dosage, and potential interactions with other medications. Store brands containing the same active ingredients as brand-name sleep aids are often available at a more affordable price, making them an attractive option for those seeking relief from occasional insomnia.
Key Takeaways
- Over the counter sleeping pills can provide relief for occasional sleepless nights but are not intended for long-term use.
- Common OTC sleep aids include antihistamines (diphenhydramine and doxylamine), melatonin, and valerian root.
- Natural sleep supplements like melatonin and valerian root may have fewer side effects compared to antihistamines.
- Store brands with the same active ingredients as brand-name sleep aids are often more affordable.
- Always consider potential side effects, interactions, and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new sleep aid.
Understanding Sleep Aids: How They Work and Their Effectiveness
In today’s fast-paced world, millions of Americans struggle with insomnia and turn to various sleep aids for relief. These non-prescription sleep medications work by producing a sedative effect, making you feel sleepy and helping you relax. Most sleep aids target specific brain receptors to slow down the nervous system, allowing you to drift off into a peaceful slumber.
While sleep aids can be a lifesaver for occasional sleepless nights, it’s essential to understand their limitations. Over time, the effectiveness of these insomnia remedies may diminish, and regular use can lead to dependence. As you navigate the world of sleep aids, remember that they are best suited for short-term use and may not provide a long-term solution for chronic insomnia.
Types of Sleep Aids and Their Mechanisms
Sleep aids come in various forms, each targeting different aspects of the sleep-wake cycle. Some popular types include:
- Melatonin supplements: These mimic the body’s natural sleep hormone, helping regulate the sleep-wake cycle.
- Antihistamines: Commonly found in OTC sleep aids, they cause drowsiness by blocking histamine receptors.
- Herbal remedies: Valerian root and chamomile are believed to have calming effects that promote relaxation.
- GABA medications: These newer sleep medicines target specific GABA receptors to induce sleepiness.
By understanding the mechanisms behind different sleep aid options, you can make an informed decision when selecting a product that aligns with your needs. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication or supplement regimen.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Effectiveness of Sleep Aids
While sleep aids can provide much-needed relief for occasional insomnia, their long-term effectiveness is questionable. Many individuals find that the sedative effects of these medications diminish over time, requiring higher doses to achieve the same results. This can lead to a cycle of dependence and potential side effects.
According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, the use of OTC sleep aids for chronic insomnia is not recommended due to the lack of long-term efficacy and the potential for adverse effects.
Instead of relying solely on sleep aids, experts recommend adopting healthy sleep hygiene habits. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime. By combining these practices with short-term use of sleep aids when necessary, you can improve your overall sleep quality and reduce your reliance on medications.
Remember, if you find yourself struggling with persistent insomnia or experiencing any adverse effects from sleep aids, it’s crucial to consult with your doctor. They can help you develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the underlying causes of your sleep issues and explores alternative options, such as cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I).
Melatonin: The Natural Sleep Hormone
Melatonin, a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland in the brain, plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Its production is closely connected to the time of day, increasing when it’s dark and decreasing when it’s light. As a result, melatonin supplements have gained popularity as a potential sleep aid, particularly for individuals struggling with jet lag or delayed sleep-wake phase disorder.
How Melatonin Supplements Work
Melatonin supplements, typically manufactured in a laboratory setting, aim to mimic the effects of the body’s natural melatonin production. By taking these supplements, individuals seek to regulate their sleep patterns and alleviate sleep-related issues. Research suggests that melatonin might slightly reduce the time it takes to fall asleep, making it a potential option for those who have difficulty initiating sleep.
Moreover, melatonin supplements have shown promise in improving circadian rhythm sleep disorders in both adults and children. For individuals with delayed sleep-wake phase disorder, melatonin can help reduce the time needed to fall asleep and advance the start of sleep. It may also alleviate symptoms associated with jet lag, such as daytime sleepiness and impaired alertness.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Melatonin
While melatonin supplements offer several potential benefits, it’s essential to consider both the advantages and disadvantages before incorporating them into your sleep routine. On the positive side, melatonin is generally considered safe for short-term use and has been shown to promote sleep in many individuals. It may also offer additional benefits, such as reducing evening confusion and restlessness in people with Alzheimer’s disease.
However, melatonin supplements can also cause side effects, including headache, dizziness, nausea, and drowsiness. It’s crucial to be aware of possible drug interactions, as melatonin may interact with various medications, such as anticoagulants, anticonvulsants, blood pressure drugs, and diabetes medications. Furthermore, individuals with autoimmune diseases should exercise caution when considering melatonin supplements due to potential risks.
Recommended Dosage and Precautions
When it comes to dosage, experts generally recommend taking 1 to 5 milligrams of melatonin approximately 30 minutes before bedtime. It’s important to start with the lowest effective dose and gradually adjust if needed. While melatonin supplements may help individuals fall asleep faster, they do not typically assist in maintaining sleep throughout the night.
Nearly two-thirds of American adults have taken melatonin supplements, and their use among children and adolescents is on the rise. However, research on the safety and efficacy of melatonin supplements for children is limited, and they are not typically recommended for those under the age of 5.
As with any supplement, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting melatonin, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should also avoid melatonin supplements unless advised otherwise by their healthcare provider.
While melatonin supplements can be a helpful tool for individuals struggling with sleep issues, it’s important to remember that they are not a sole treatment for insomnia. Combining melatonin with other therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or relaxation techniques, may provide a more comprehensive approach to improving sleep quality and duration.
Antihistamines as Sleep Aids: Diphenhydramine and Doxylamine
When you’re struggling to get a good night’s sleep, you might turn to over-the-counter (OTC) sleep aids for relief. Two common antihistamines used as sleep aids are diphenhydramine and doxylamine, which can be found in popular products like Benadryl and Unisom. While these medications may help you drift off to dreamland, it’s essential to understand how they work and their potential side effects.
How Antihistamines Induce Sleepiness
Diphenhydramine and doxylamine are first-generation antihistamines that cross the blood-brain barrier and bind to histamine receptors in the brain, causing drowsiness. They also have anticholinergic properties, which can lead to additional side effects. While these medications can be effective for short-term insomnia relief, they are not recommended for long-term use due to the potential for tolerance and side effects.
The sedative effect of diphenhydramine can last for up to seven hours, while doxylamine succinate tends to work longer, for up to eight hours. The recommended dose of diphenhydramine for adults and children 12 and over is 50 milligrams at bedtime, while diphenhydramine citrate may require a dose of up to 76 mg. For doxylamine succinate, the recommended dose for adults and children over 12 is 25 mg taken 30 minutes before bedtime.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
While antihistamines can be effective for short-term insomnia relief, they come with a range of potential side effects. Some common side effects of diphenhydramine and doxylamine include:
- Daytime drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Urinary retention
- Blurred vision
- Nausea
- Headache
More severe side effects may occur in individuals with certain health conditions, such as narrow-angle glaucoma, enlarged prostate, or breathing problems. First-generation antihistamines are also not recommended for adults aged 65 and older due to the increased risk of side effects like confusion and balance problems. Additionally, research suggests that the anticholinergic properties in these medications may increase the risk of dementia in older adults.
It’s important to note that tolerance to the sedative effects of antihistamines can develop quickly with frequent use, reducing their effectiveness as sleep aids over time. Chronic insomnia should not be treated with OTC antihistamines; instead, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate management of ongoing sleep problems.
| Medication | Common Brand Names | Recommended Dose | Duration of Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diphenhydramine | Benadryl, Unisom, Advil PM | 50-76 mg at bedtime | Up to 7 hours |
| Doxylamine Succinate | Unisom SleepTabs, Nighttime Cold & Flu Relief | 25 mg 30 minutes before bedtime | Up to 8 hours |
If you’re considering using antihistamines for sleep, it’s essential to talk to your doctor or pharmacist to ensure they are safe and appropriate for you. They can help you weigh the potential benefits and risks, as well as recommend alternative strategies for improving sleep quality, such as practicing good sleep hygiene or exploring other treatment options like cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I).
Herbal Sleep Remedies: Valerian and Kava
When it comes to natural sleep supplements, valerian root and kava stand out as two popular herbal sleep medicines. Valerian root, derived from the perennial flowering plant Valeriana officinalis, has been used for centuries to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. This herbal remedy is believed to work by increasing the levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain, which has a calming effect on the nervous system.
Studies have shown that valerian root can be an effective natural sleep aid, with some research suggesting that taking valerian over a period of time (such as four weeks) may be more beneficial than taking it for just one night. The recommended dosage for valerian root typically ranges from 300–600 mg, taken up to 2 hours before bedtime. It is generally well-tolerated for up to a month to six weeks in most cases, making it a suitable option for those seeking a natural approach to better sleep.
Kava, another herbal sleep remedy, is a member of the pepper family native to the South Pacific islands. Kava contains compounds called kavalactones, which appear to activate GABA receptors in the brain, promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety. However, it is essential to note that reports from Europe indicate over 20 cases of cirrhosis, hepatitis, and liver failure possibly associated with kava use, so caution should be exercised when considering this herbal sleep aid.
“Nearly half of Americans sometimes have trouble with sleep, and many turn to natural sleep supplements like valerian root and kava for relief. While these herbal remedies show promise, it’s crucial to discuss their benefits and risks with a healthcare professional before incorporating them into your sleep routine.”
When considering herbal sleep medicines, it is important to keep in mind that these natural sleep supplements may not undergo pre-market evaluation and approval by the FDA. This lack of regulation can pose risks of inappropriate dosing, which can be dangerous, especially for certain demographic groups. Experts recommend discussing the benefits and risks of herbal sleep remedies with a doctor to make informed decisions about their usage and ensure the safest and most effective approach to improving sleep quality.
| Herbal Sleep Remedy | Recommended Dosage | Potential Benefits | Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valerian Root | 300–600 mg, up to 2 hours before bedtime | Increases GABA levels, promotes relaxation, improves sleep quality | Well-tolerated for up to 6 weeks, may interact with certain medications |
| Kava | Varies depending on preparation | Activates GABA receptors, reduces anxiety, promotes relaxation | Reports of liver damage, should be used with caution |
In summary, valerian root and kava are two popular herbal sleep medicines that offer potential benefits for those seeking natural ways to improve their sleep. However, as with any sleep supplement, it is crucial to approach their use with caution, consult with a healthcare professional, and prioritize overall sleep hygiene for the most effective and sustainable path to better rest.
Over the Counter Sleeping Pills: Brands, Formulations, and Effectiveness
When it comes to finding relief from occasional sleeplessness, many Americans turn to over the counter (OTC) sleeping pills. These sleep aid brands offer a variety of formulations designed to help you drift off to dreamland more easily. But with so many options available, it can be challenging to determine which one is right for you.
Popular OTC Sleep Aid Brands
Some of the most well-known OTC sleep aid brands include Benadryl, Unisom, ZzzQuil, Advil PM, and Tylenol PM. These products often contain antihistamines like diphenhydramine or doxylamine succinate, which can cause drowsiness and help you fall asleep more quickly. However, it’s important to note that these medications are not intended for long-term use and may cause side effects such as grogginess, dry mouth, and dizziness.
Comparing Ingredients and Formulations
OTC sleep aids come in a wide range of forms, including gummies, pills, powders, drinks, teas, capsules, and tinctures. Some products contain natural ingredients like melatonin, valerian root, chamomile, or L-theanine, while others rely on pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen in combination with antihistamines.
When comparing different OTC sleep aid formulations, it’s essential to consider your individual needs and preferences. For example, if you have difficulty swallowing pills, a liquid or gummy form may be more appealing. If you’re sensitive to certain ingredients or have allergies, be sure to read the labels carefully and consult with your doctor before trying any new sleep aid.
| Brand | Active Ingredient(s) | Form |
|---|---|---|
| Benadryl | Diphenhydramine | Tablets, Capsules, Liquid |
| Unisom SleepTabs | Doxylamine Succinate | Tablets |
| ZzzQuil | Diphenhydramine | Liquid, LiquiCaps |
| Advil PM | Diphenhydramine, Ibuprofen | Caplets |
| Tylenol PM | Diphenhydramine, Acetaminophen | Caplets |
User Reviews and Experiences
When evaluating the effectiveness of OTC sleep aids, it can be helpful to read user reviews and learn from the experiences of others. Keep in mind that everyone’s body is different, and what works for one person may not work for another.
“I’ve tried several different OTC sleep aids, and I find that melatonin gummies work best for me. They help me fall asleep more quickly without leaving me feeling groggy in the morning.” – Sarah, 32
“I occasionally use Benadryl when I’m having trouble sleeping due to allergies or a cold. It definitely makes me drowsy, but I try not to rely on it too often because I don’t want to become dependent.” – Michael, 45
Ultimately, the most effective OTC sleep aid for you will depend on your specific needs, preferences, and overall health. If you find that OTC products are not providing the relief you need or if you’re experiencing persistent insomnia, it’s important to speak with your doctor to rule out underlying health issues and discuss alternative treatment options.
Safety Precautions and Potential Risks of OTC Sleep Aids
While over-the-counter sleep aids can provide much-needed relief for those struggling with occasional sleeplessness, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential risks and take necessary safety precautions. By understanding the interactions, side effects, and dependency concerns associated with these medications, you can make informed decisions about your sleep aid use and know when it’s time to consult a doctor for personalized guidance.
Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
One of the most important aspects of sleep aid safety is being mindful of interactions with other medications and substances. Many OTC sleep aids contain antihistamines, which can interact with alcohol, certain antidepressants, and other medications, potentially leading to dangerous side effects. It’s essential to read the labels carefully and consult with a healthcare professional if you’re taking any other medications or have pre-existing health conditions. Remember, combining sleep aids with alcohol can be particularly hazardous, as it may cause excessive drowsiness and impair cognitive function.
Dependency and Tolerance Concerns
While OTC sleep aids are generally considered safe for short-term use, long-term reliance on these medications can lead to tolerance and potential dependency issues. Over time, your body may develop a tolerance to the active ingredients, requiring higher doses to achieve the same sleep-inducing effects. This can be problematic, as higher doses may increase the risk of side effects and make it more difficult to stop using the sleep aid. To minimize the risk of developing tolerance or dependency, it’s recommended to use OTC sleep aids only as directed and for the shortest duration possible. Incorporating natural sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and creating a conducive sleep environment, can help reduce the need for long-term sleep aid use.
“Approximately 8 out of 10 people experience a hangover effect the day after taking sleep medicine, leading to drowsiness, muddled thinking, and balance problems.”
When to Consult a Doctor
If you find yourself relying on OTC sleep aids for more than a week or two, it’s important to consult with a doctor to address any underlying issues that may be contributing to your sleep troubles. Chronic insomnia can be a symptom of various health conditions, such as sleep apnea, anxiety, or depression, which may require specialized treatment. Additionally, if you experience any unusual or severe side effects while using OTC sleep aids, such as hallucinations or allergic reactions, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Your doctor can help you determine the best course of action and recommend alternative treatments or lifestyle changes to improve your sleep quality without the need for medication.
It’s also worth noting that certain populations, such as the elderly, heart patients, and cancer patients, may be at a higher risk for adverse effects when using sleep aids. In these cases, it’s especially important to explore non-drug treatments first and consult with a healthcare provider before considering any sleep medications. By prioritizing sleep aid safety and being proactive about addressing sleep issues, you can take steps towards achieving more restful, rejuvenating sleep without compromising your overall health and well-being. Remember, a quality sleeping pillow can also play a significant role in promoting better sleep and reducing the need for sleep aids.
| Population | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Elderly individuals | Explore nondrug treatments first due to increased risks of confusion and balance problems that can lead to falls |
| Heart patients | Try alternative methods like changing sleep environment or cognitive behavioral therapy before considering sleeping pills due to long-term risks |
| Cancer patients | Explore alternative methods for better sleep, with healthcare providers possibly suggesting cognitive behavioral therapy and Z-drugs if sleep problems persist |
Natural Sleep Hygiene Tips to Complement OTC Sleep Aids
While over the counter sleeping pills can provide temporary relief for sleep issues, incorporating natural sleep hygiene practices can enhance their effectiveness and promote better overall sleep quality. By establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a conducive sleep environment, and employing relaxation techniques and stress management strategies, you can optimize the benefits of OTC sleep aids and improve your sleep hygiene.
Establishing a Regular Sleep Schedule
One of the most crucial aspects of sleep hygiene is maintaining a consistent sleep schedule. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends, helps regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally. Aim to establish a bedtime that allows for the recommended amount of sleep based on your age group. According to the CDC, adults 18 to 60 years old should get seven or more hours of sleep, while those 60 to 64 years old should get seven to nine hours, and adults over 65 years old should aim for seven to eight hours.
In addition to setting a regular sleep schedule, it’s important to avoid caffeine and daytime naps, as these can interfere with your ability to fall asleep at night. Regular exercise can also contribute to better sleep, but be sure to finish your workout at least a few hours before bedtime to allow your body time to wind down.
Creating a Conducive Sleep Environment
Your sleep environment plays a significant role in the quality of your sleep. To create a space that promotes relaxation and restfulness, ensure that your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Invest in a comfortable mattress, pillows, and bedding that support your body and help you feel at ease. Avoid using electronic devices with lighted screens, such as smartphones or tablets, for at least an hour before bedtime, as the blue light emitted by these devices can disrupt your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
| Sleep Environment Factor | Recommended Conditions |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 60-67°F (15-19°C) |
| Noise Level | Quiet or white noise |
| Lighting | Dark or dimly lit |
| Bedding | Comfortable, supportive mattress and pillows |
Relaxation Techniques and Stress Management
Stress and anxiety can significantly impact your ability to fall asleep and maintain restful sleep throughout the night. Incorporating relaxation techniques and stress management strategies into your bedtime routine can help calm your mind and body, making it easier to drift off to sleep. Some effective relaxation techniques include:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Mindfulness meditation
- Gentle yoga stretches
A small body of research indicates that L-Theanine supplements can reduce stress and anxiety, enhance relaxation, and improve sleep.
In addition to these techniques, practicing good stress management throughout the day can contribute to better sleep at night. This may include regular exercise, time management, and engaging in hobbies or activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
By combining natural sleep hygiene practices with the judicious use of OTC sleep aids, you can create a comprehensive approach to improving your sleep quality and overall well-being. Remember, if sleep issues persist or worsen despite these efforts, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further guidance and support.
Alternatives to Over the Counter Sleeping Pills
While over-the-counter sleep aids can provide temporary relief for occasional sleepless nights, they may not be the best long-term solution for chronic insomnia. If you find that OTC sleep aids are not effectively improving your sleep quality or duration, it’s important to explore alternative options that can address the underlying causes of your sleep issues.
Prescription Sleep Medications
For individuals with persistent insomnia, prescription sleep medications may be recommended by a healthcare professional. These medications are typically more potent than OTC sleep aids and are designed to target specific sleep disorders. Your doctor will assess your medical history, symptoms, and overall health to determine if prescription sleep medications are appropriate for your situation. It’s crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and duration of use to minimize potential side effects and dependency risks.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is a non-pharmacological approach that has proven to be highly effective in treating chronic insomnia. CBT-I focuses on identifying and modifying thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors that contribute to sleep difficulties. Through structured sessions with a trained therapist, you’ll learn techniques to establish healthier sleep habits, create a more conducive sleep environment, and manage stress and anxiety related to sleep. CBT-I equips you with long-term strategies to improve sleep quality and duration without relying on medication.
In some cases, a sleep study may be recommended to gain a comprehensive understanding of your sleep patterns and identify any underlying sleep disorders. During a sleep study, your brain waves, movements, and breathing are monitored overnight, providing valuable insights into potential issues that may not be apparent during a routine medical evaluation. The results of a sleep study can help guide your healthcare provider in developing a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs, whether it involves prescription sleep medications, CBT-I, or a combination of both.